The GRID Access Layer is an Apache Maven project and therefore has to be built with Maven. This guide is a "Quick Start" guide to build the project, is does not replace the more detailed information that can be found at "http://maven.apache.org/".
Maven is a build, build-project and package management software. Based on the "pom.xml" files (project descriptors) it auto-downloads everything what is needed on top of a plain maven installation and stores it inside a local maven repository which is located at "%HOMEPATH%\.m2" or "~/.m2".
When used for building, maven can build multi-module projects including aggregated information like this information site, apidocs and project reports along with the resulting application. Also Unit testing frameworks and CI frameworks can easily be integrated.
Maven manages the full build cycle including dependencies and deployment.
The basic mavenized package & build-project management functionality is built-into Intellij IDEA even without an installed Maven, as the IDE can use the "pom.xml" files to manage the software project.
The IDE can now also be used to build the project but without a Maven installation it can't build any Maven goals. What can be achieved is building the project using the IDE's own logic which is sophisticated enough to run & debug Unit tests and also the full server.
An opensource version of the IDE that is capable of handling POJOs and Maven projects can be obtained from http://www.jetbrains.com/idea/, however it's a recommendation to use the paid version of the IDE to obtain more advanced support for Frameworks like JPA, Spring and others.
No IDE is required for building the project only. The build just depends on Maven. So the first step is to prepare & install Maven once.
A maven installation itself is nothing complicated:
Apache Maven 2.2.1 (r801777; 2009-08-06 21:16:01+0200) Java version: 1.6.0_16 Java home: C:\Projects\DevEnv\jdk64\jre Default locale: de_DE, platform encoding: Cp1252 OS name: "windows 7" version: "6.1" arch: "amd64" Family: "windows"
Once Maven is installed the access layer can be built using the provided "make.bat". If the build fails make sure the build-machine has the correct environment settings and has a public Internet connection.
cd \Path\To\AccessLayer make.bat <<< check build output >>> cd target\bin-app.dir <<< collect final application from here >>>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>>>>> Trend Micro - GRID Access Layer - How To Build <<<<<
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
About
The GRID Access Layer (GACL) is a Maven 2.2 based project.
Building follows in general the standard rules of any Maven 2.2 project as
it is documented @ http://maven.apache.org/
As a summary, the prerequisites on a build machine are:
- An installed JDK >= 1.6 (best 64bit but not required)
- An installed Maven 2.2 ("mvn -version" returns >= 2.2)
Building
The easiest way to build the access layer is to use the "make.bat" file
and build it under Microsoft Windows. However as the build system is
not bound to a platform, it builds successfully also under Linux or
Mac using "mvn" directly (see sections below).
After installing the JDK and Maven run:
make.bat
Once the build finished, all results can be taken from the folder
"target/access-layer-[version]-dist" or one of the archives.
Note: The folder "target/access-layer-[version]-dist/webapps/doc" contains
a detailed project documentation (Project site) with more in depth
information on what the ACL is all about. This documentation is built out
of sources contained in the "site" directories and only available after
the build succeeded.
If the build fails, verify that:
"java -version" returns something similar to:
java version "1.6.0_16"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.6.0_16-b01)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 14.2-b01, mixed mode)
"mvn -version" returns something similar to:
Apache Maven 2.2.1 (r801777; 2009-08-06 21:16:01+0200)
Java version: 1.6.0_16
Java home: C:\Projects\DevEnv\jdk64\jre
Default locale: de_DE, platform encoding: Cp1252
OS name: "windows 7" version: "6.1" arch: "amd64" Family: "windows"
The build machine has enough spare resources (RAM > 1024, Disk > 4GB)
Building with "mvn"
Multi-module Maven projects are setup hierarchically forming a tree
of modules with dependencies. The root POM is the one located inside
the root folder of the Access Layer project.
Previous versions of the ACL required 2 separate build steps to
generate all dependencies in the right order. Since version 1.1
this is no longer required.
1. Build a fresh application assembly (and install the artifacts):
> mvn clean install
2. Build only the changed artifacts:
> mvn install
3. Quick Build without reports and documentation site (3 x times faster)
> mvn install -Dskip.site=true
Note: The default JRE resource settings may not be sufficient when
building with Maven. It may be required to set the following environment
variable in the scope before executing a build:
MAVEN_OPTS=-Xms256m -Xmx512m -XX:MaxPermSize=256m
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(C) Trend Micro Inc. 2010
The project is setup as a Maven 2.2 multi-module project following the default directory layout for maven projects with the exception that the "site" folder is not contained below the "src" folder in order to simplify creating a main site.
Below is an overview of the most important files and folder including the 2 main pom.xml files:
.idea/ - Intellij IDEA Project Files
config/ - Configuration files and parent poms
assemblies/ - Assembly descriptors defining the final ACL package layout.
defaults/ - Contains statically dumped configurations (from Sonar) for
code quality analysis tools.
doc/ - Additional static documentation, data sheet & concept.
server-application/ - The actual modules of the access layer.
site/ - The main information site (documentation)
site-skin/ - Contains the skin used for building the documentation pages.
target/ - The build output (may be missing initially and should
NEVER be submitted to any VCS systems)
testsuite/ - A collection of modules that are used to develop CI and
synthetic (e.g. load) tests for the ACL.
pom.xml - The ROOT pom for the Access Layer Project.
AccessLayer.iml - The Intellij IDEA module file for the root module.
makeSite.bat - Makes the information site.
make.bat - Makes everything in the correct build order.
When using IntelliJ IDEA >= 8, there are existing run & debug configurations that can be used in order to Run and Debug the ACL completely from within the IDE.
See the following screenshot for a sample Setup:
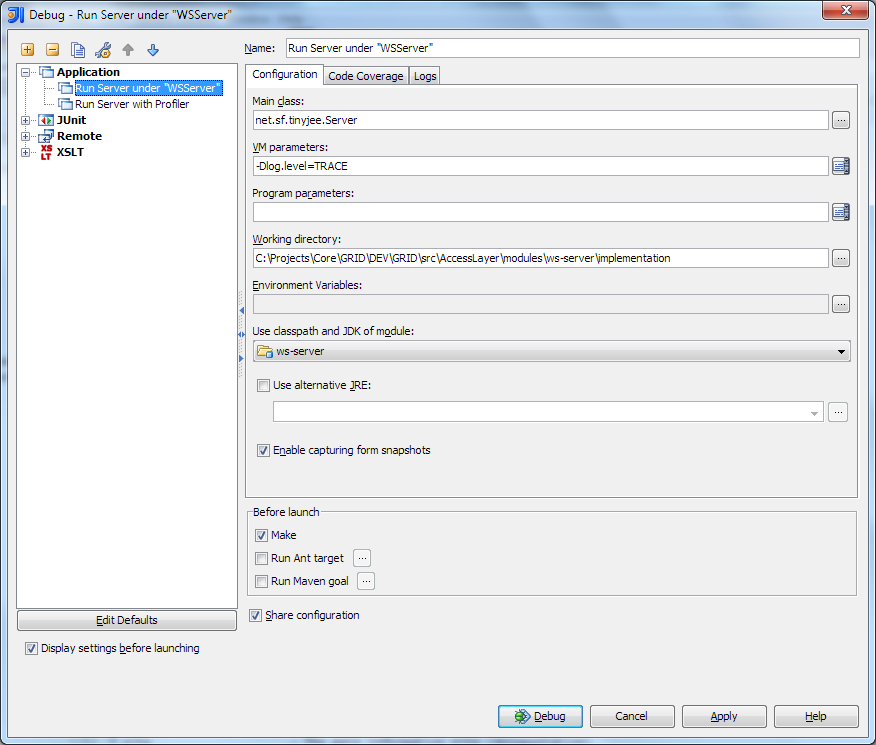
These settings will work in any Java IDE, it's not limited to IntelliJ IDEA. The important values to set are:
When using IntelliJ IDEA, code navigation is enabled by holding the CTRL key and moving the mouse over the symbols to navigate to. Pressing CTRL-Q will display code help for the symbol under the caret.
Maven 2 has built-in support for various test frameworks including JUnit4. Built-in support means that a special source path is defined that is used to host the test classes and a test runner exists that can auto-detect test classes and execute them during a build.
Attention: Failing a unit test breaks the build by default. Please run unit tests locally using mvn test before submitting changes to perforce.
Unit tests for this project are following the standard of JUnit 4.8 (The JUnit version is defined inside "config/defaults/pom.xml") and must be placed inside the source path for test classes as defined by Maven 2.
In order to create and run Unit tests follow the standard tutorials & documentation for JUnit 4 and Maven:
When using a Maven 2 aware IDE, tests classes can usually be auto-created using the IDEs JUnit support. Within IntelliJ IDEA, test can be generated by placing the caret on the name of the class to test and pressing ALT-RETURN to show the intention actions and select Create Test afterwards.
Please take care to create JUnit4 tests (JUnit3 is not compatible) inside the "test" path. In addition test classes should be named with the keyword "Test" at the end to make them easier to discover.
Note: The name of the test class has no effect on whether it's executed or not, the build system will execute all public, non-abstract classes that exist inside the "test" path.
A standard test-class for the class "com.trendmicro.grid.MySampleAction" looks like:
package com.trendmicro.grid;
import org.junit.*;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* TODO: Create Description.
*
* @author Author, 2010-08-12
* @version 1.0
*/
public class MySampleActionTest {
MySampleAction action;
@Before
public void setUp() {
action = new MySampleAction();
}
@Test
public void testDoSomethingDoesSomething() {
fail("Test is missing");
}
}
Unit tests can easily be run or debugged from within the IDE using a standard JUnit run & debug configuration. (From within IntelliJ IDEA it's enough to right click a test class and create a new "Test-Run Configuration" in order to run the test)
The used application server TinyJEE offers a special test runner that can be used in conjunction with JUnit4 allowing to execute tests in a fully functional server environment.
Using this feature allows developing tests that can simulate all use cases that external modules may be raising against the access layer (including SOAP & REST calls) and effectively it allows to:
In order to simplify the process and ensure the system is running with correct settings, this type of tests should be exclusively created inside the module "ws-server" and the should be placed in the packages: "com.trendmicro.grid.acl.l0.integrationtest" or "com.trendmicro.grid.acl.l0.regressiontest".
In addition the tests must either directly or indirectly derive from the abstract base class "com.trendmicro.grid.acl.l0.AbstractServiceTestBase":
package com.trendmicro.grid.acl.l0;
import ch.qos.logback.classic.Level;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.commons.Hex;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.commons.Paths;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.commons.Utils;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.commons.XmlSerializer;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.ds.RepositoriesContext;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.ds.RepositorySelector;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.l0.client.PublicAuthenticationServiceClient;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.l0.datatypes.ProcessPackageDataSet;
import com.trendmicro.grid.acl.metadata.ValidationContext;
import net.sf.tinyjee.spring.test.TinyJEESpringJUnit4Runner;
import net.sf.tinyjee.streams.ByteBufferOutputStream;
import net.sf.tinyjee.streams.PositionInputStream;
import net.sf.tinyjee.test.Property;
import net.sf.tinyjee.test.TestConfiguration;
import net.sf.tinyjee.test.TinyJEEJUnit4Runner;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
/**
* Is a base class for all test classes that need to run inside a full
* application server environment.
*
* @author juergen_kellerer, 2010-05-14
* @version 1.0
*/
@ContextConfiguration
@RunWith(TinyJEESpringJUnit4Runner.class)
@TestConfiguration(
value = {
@Property(name = "bitronix.tm.disableJmx", value = "true"),
@Property(name = "gacl.3rdcache.is.synchronous", value = "true"),
/*@Property(name = "gacl.3rdcache.enable-persistence", value = "true"),*/
// required for Case335Test
@Property(name = "gacl.accept.results.on.final.jobs", value = "true")
},
// Frameworks like hibernate, etc. are set to WARN level. Switch to DEBUG only for temporary purposes.
logLevelFrameworks = "WARN", logLevel = "WARN")
public abstract class AbstractServiceTestBase {
@Resource
PublicAuthenticationServiceClient authenticationServiceClient;
PublicAuthenticationService authenticationService;
static Random random = new Random();
static PrintWriter timedRunsLog;
static {
try {
timedRunsLog = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("~timed-test-runs.log", true), true);
timedRunsLog.println("UnitTests Started: " + new Date());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
private static File dummyFileStore;
@BeforeClass
public static void setLogLevelToDebug() {
// Note: Using DEBUG log to ensure log calls are performed and will not fail when enabled in a production environment.
final ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger logger =
(ch.qos.logback.classic.Logger) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory().getLogger("com.trendmicro");
logger.setLevel(Level.DEBUG);
}
@Before
public void login() throws Exception {
authenticationService = authenticationServiceClient.getLocalPort();
authenticationService.authenticate("okuser", "okpassword");
}
@After
public void logout() throws Exception {
authenticationService.logout();
}
/**
* Returns a random number generator.
*
* @return a random number generator.
*/
public static Random getRandom() {
return random;
}
/**
* Returns the path to the dummy file store.
*
* @return the path to the dummy file store.
*/
public static File getDummyFileStore() {
if (dummyFileStore == null) {
dummyFileStore = new File(Paths.getResourcePath(), "/dummy-file-repository");
if (!dummyFileStore.isDirectory())
dummyFileStore.mkdirs();
}
return dummyFileStore;
}
/**
* Returns a file from the dummy file repository.
*
* @param sha1 the sha1 hash of the file to get.
* @param create whether the file should be created or just returned.
* @return a file from the dummy file repository.
*/
public static File getFileFromDummyFileStore(byte[] sha1, boolean create) {
final File dummyFile = new File(getDummyFileStore(), Hex.encode(sha1) + ".data");
if (create) {
if (dummyFile.exists() && !dummyFile.delete())
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot delete file " + dummyFile + ", it's in the way.");
try {
if (!dummyFile.createNewFile())
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot create file " + dummyFile + ".");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(dummyFile.toString(), e);
}
}
return dummyFile;
}
/**
* Prints a measurement tag to stdout which may be used with the Jenkins plugin 'Measurement Plots'.
*
* @param uniqueName the unique name of the measurement to print.
* @param value the value to print.
*/
public static void printMeasurement(String uniqueName, double value) {
System.out.printf("<measurement><name>%s</name><value>%f</value></measurement>%n", uniqueName, value);
}
/**
* Returns a byte array with random data of the specified length.
*
* @param length the length of the random byte array to create.
* @return a byte array with random data of the specified length.
*/
public static byte[] createTestData(int length) {
byte[] b = new byte[length];
random.nextBytes(b);
return b;
}
/**
* Returns the HTTP port number of the running application server instance.
*
* @return the HTTP port number of the running application server instance.
*/
public static int getLocalServerPort() {
return Integer.getInteger("tinyjee.connection.http.port");
}
/**
* Returns the HTTPS port number of the running application server instance.
*
* @return the HTTPS port number of the running application server instance.
*/
public static int getLocalSecureServerPort() {
return Integer.getInteger("tinyjee.connection.https.port");
}
/**
* Returns a new HTTP url pointing to the specified path on the running
* application server instance.
*
* @param path the path to point the to.
* @return a new HTTP url pointing to the specified path.
*/
public static URL getLocalHttpURL(String path) {
try {
return new URL("http", "127.0.0.1", getLocalServerPort(), path);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Resource
protected RepositoriesContext context;
/**
* Selects the activated repsitory implementations based on a list of
* implementation name artifacts.
* <p/>
* Note: The list is processed from left to right. Selection made earlier
* can get overwritten by selection made later.
*
* @param keys a list of implementation name artifacts to try to select.
*/
protected void selectRepositories(String... keys) {
for (String key : keys) {
for (RepositorySelector<?> selector : context.getAllSelectors())
for (String availableKey : selector.getAvailableKeys())
if (availableKey.contains(key)) {
selector.setSelectedKey(availableKey);
break;
}
}
}
/**
* Clears the test database.
*
* @param em the entity manager to use for executing the statements.
*/
protected void clearTestDataBase(EntityManager em) {
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM PACKAGE_FILES_HISTORY").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM PACKAGE_FILES").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM PACKAGE_HISTORY").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM PACKAGES").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM FILE_CONTENT_HISTORY").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM FILE_CONTENT_STATISTICS").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM FILE_CONTENT_SOURCES").executeUpdate();
em.createQuery("DELETE FROM FILE_CONTENTS").executeUpdate();
em.flush();
}
/**
* Clears the the entity manager (removing any cached entries).
*
* @param em the entity manager to clear.
*/
protected void clearEntityManager(EntityManager em) {
em.flush();
em.clear();
//causes lock timeout
//em.getEntityManagerFactory().getCache().evictAll();
}
/**
* Uses HTTP-PUT to send the specified binary data against the specified url.
*
* @param uploadURL the url to send the data to.
* @param data the data to send.
* @throws Exception in case of the operation failed for any reason.
*/
protected void putData(URL uploadURL, byte[] data) throws Exception {
final HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) uploadURL.openConnection();
urlConnection.setChunkedStreamingMode(512);
TinyJEEJUnit4Runner.Utils.putContent(urlConnection, new ByteArrayInputStream(data));
}
/**
* Uses HTTP-GET to get the binary data of the specified url.
*
* @param downloadURL the url to download.
* @return the downloaded data as byte array.
* @throws Exception in case of the operation failed for any reason.
*/
protected byte[] getData(URL downloadURL) throws Exception {
return TinyJEEJUnit4Runner.Utils.getContent(downloadURL);
}
/**
* Clones the given dataset using XML serialization and de-serialization.
*
* @param other the dataset to clone.
* @return the cloned dataset.
* @throws Exception in case of the XML serialization failed.
*/
protected static ProcessPackageDataSet clone(ProcessPackageDataSet other) throws Exception {
XmlSerializer<ProcessPackageDataSet> serializer = ProcessPackageDataSet.getXmlSerializer();
ByteBufferOutputStream buffer = new ByteBufferOutputStream();
serializer.save(other, buffer);
return serializer.load(buffer.asInputStream());
}
/**
* Decodes all process package dataSets from the given zip.
*
* @param in The zip to read from.
* @param suffixes a set of suffixes identifying the files to read.
* @return the decoded process package dataSets.
* @throws Exception In case of decoding failed.
*/
protected List<ProcessPackageDataSet> readDataSetsFromZip(InputStream in, String... suffixes) throws Exception {
if (suffixes.length == 0)
suffixes = new String[]{".xml"};
List<ProcessPackageDataSet> storedDataSets = new ArrayList<ProcessPackageDataSet>();
XmlSerializer<ProcessPackageDataSet> serializer = ProcessPackageDataSet.getXmlSerializer();
ZipEntry e;
ZipInputStream zIn = new ZipInputStream(in);
try {
while ((e = zIn.getNextEntry()) != null) {
for (String pattern : suffixes) {
if (e.getName().endsWith(pattern)) {
storedDataSets.add(serializer.load(new PositionInputStream(zIn, false)));
break;
}
}
}
} finally {
zIn.close();
}
return storedDataSets;
}
/**
* Prints the time the runnable took to complete.
*
* @param t the runnable to run.
* @param runs the number of runs to time.
* @param title the title describing what the runnable tests.
*/
protected void timedTestRun(Runnable t, int runs, String title) {
long time = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < runs; i++)
t.run();
double durationSeconds = Utils.calculateNanoDurationInSeconds(time);
String line = String.format("%02d runs ; duration %s: '%s'%n", runs, Utils.formatNanoDuration(time), title);
synchronized (System.out) {
System.out.print(line);
timedRunsLog.print(line);
printMeasurement(title, durationSeconds);
}
}
/**
* Runs the specified callable with as many threads concurrently as specified.
*
* @param threadCount The number of threads to use for running the callable.
* @param testCode The test code to run.
* Note: The method must return true if the test was successful.
* Assertion methods are NOT supported.
* @throws Throwable In case of the callable was throwing an exception or when the threads got interrupted.
*/
protected void runTestWithMultipleThreads(int threadCount, final Callable<Boolean> testCode) throws Throwable {
runTestWithMultipleThreads(threadCount, testCode, 0);
}
/**
* Runs the specified callable with as many threads concurrently as specified.
*
* @param threadCount The number of threads to use for running the callable.
* @param testCode The test code to run.
* Note: The method must return true if the test was successful.
* Assertion methods are NOT supported.
* @param threadDelay Is the delay to add between the startup of the threads.
* @throws Throwable In case of the callable was throwing an exception or when the threads got interrupted.
*/
protected void runTestWithMultipleThreads(int threadCount, final Callable<Boolean> testCode,
long threadDelay) throws Throwable {
final CountDownLatch startSignal = new CountDownLatch(1), readySignal = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
final BlockingQueue<Boolean> results = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Boolean>(threadCount);
final AtomicReference<Throwable> throwable = new AtomicReference<Throwable>();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final long delayMS = i * threadDelay;
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
boolean success = false;
try {
// Waiting for a syncronized start signal.
readySignal.countDown();
startSignal.await();
// If we have a fixed delay between threads, apply it now.
if (delayMS > 0)
sleep(delayMS);
// Execute the test code.
success = testCode.call();
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
throwable.set(t);
} finally {
try {
results.put(success);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
interrupt();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
// Waiting for the threads to get initialized.
readySignal.await();
Thread.yield();
// Starting the threads now
startSignal.countDown();
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++)
assertTrue(testCode.toString(), results.take());
final Throwable t = throwable.get();
if (t != null)
throw t;
}
/**
* Disables the Metadata validation within the Test thread.
*/
@Before
public void disableMetadataValidation() {
ValidationContext.getInstance().disableValidation();
}
}
The code that is actually responsible for starting the application server before running the unit tests can be isolated to:
@RunWith(TinyJEESpringJUnit4Runner.class)
@ContextConfiguration({"property:log.level=WARN", "property:log.level.frameworks=ERROR"})
All test classes that are directly or indirectly annotated with these 2 lines will automatically run inside an application server environment. Please note that the server is started only once for the first occurrence of a test class that requires it.
ContextConfiguration allows to set server commandline parameters (like VM Parameters) and has currently one important limitation. It is not possible to use multiple different configurations under one "test" path. An attempt to do so will fail the test execution as the server is started only once and cannot be re-configured when it's already running.
Another note is that the server environment heavily depends on the features that were enabled with the configured classpath (pom dependencies). Therefore using the server environment in other modules than "ws-server" may lead to the effect of having only a partial server environment available.
When the application server is started it follows the same rules as the "Run & Debug" configurations do. Please make sure that you configure the working directory to point to the module's base directory when executing tests from within the IDE. Check the "Troubleshooting" section above for more details.